Orbital decompression surgery stands as a pivotal intervention for patients suffering from thyroid eye disease, Graves’ disease, orbital abscess or other conditions causing orbital congestion and compression. The conventional approach to this surgery involved external incisions, but recent advancements have ushered in a minimally invasive technique – endoscopic orbital decompression surgery. This blog post aims to explore the nuances, advantages, and considerations associated with this innovative procedure.
Understanding Endoscopic Orbital Decompression Surgery:
Endoscopic orbital decompression surgery involves using a small endoscope, a thin tube equipped with a camera, to access and navigate the intricate structures within the orbit. By entering through the nose or eyelid, surgeons gain a direct view of the affected orbital tissues without making external incisions.
Benefits of Endoscopic Approach:
- Minimally Invasive: The key advantage lies in its minimally invasive nature, resulting in reduced trauma, quicker recovery, and potentially lower risk of complications compared to traditional open surgeries.
- Precision and Visualization: The endoscope provides high-definition visuals, allowing surgeons to navigate delicate structures with enhanced precision, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
- Customization: Surgeons can tailor the procedure to address specific areas of congestion, ensuring a more personalized and targeted decompression.
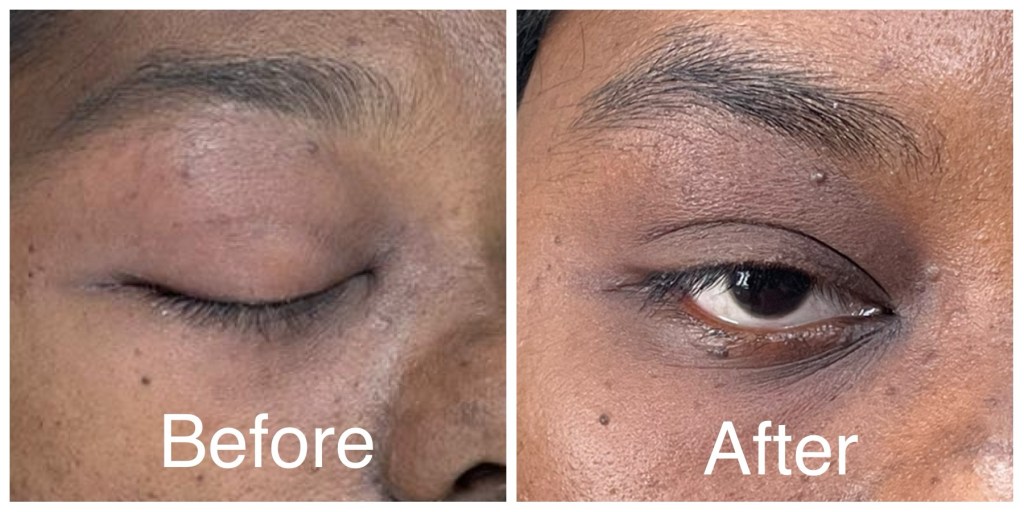
Considerations and Potential Risks:
While endoscopic orbital decompression surgery offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to consider potential risks and limitations:
- Expertise: This technique demands a high level of skill and expertise from the surgical team due to the intricate nature of the procedure.
- Anatomical Variations: Variations in individual anatomy may present challenges during the surgery, requiring adaptability and experience on the part of the surgeon.
- Postoperative Care: Patients must adhere strictly to postoperative care instructions to minimize the risk of complications such as bleeding, infection, or damage to nearby structures.
Patient Expectations and Recovery:
Patients undergoing endoscopic orbital decompression surgery can typically expect a shorter recovery period compared to traditional surgeries. However, it’s crucial to manage expectations, as full recovery might still take several weeks to months. Follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress and address any concerns promptly.
Conclusion:
Endoscopic orbital decompression surgery represents a significant advancement in the treatment of orbital conditions, offering patients a less invasive and potentially more precise option for relieving orbital pressure and improving symptoms. While it presents distinct advantages, a thorough discussion between the patient and the healthcare team is crucial to determine the most suitable approach based on individual circumstances.
As with any medical procedure, thorough evaluation, consideration of risks and benefits, and collaboration between patient and healthcare provider are vital before proceeding with endoscopic orbital decompression surgery.
Please note that this article provides general information and should not substitute professional medical advice. Patients considering this procedure should consult with an ENT surgeon to discuss individualized treatment options.
