Otitis externa, commonly known as swimmer’s ear, is an infection that affects the ear canal. It is a prevalent condition, particularly during the summer months when people spend more time swimming and engaging in water-related activities. Otitis externa can cause discomfort and pain, but with proper understanding and management, it can be effectively treated. In this blog post, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for otitis externa.
Causes of Otitis Externa: Otitis externa typically occurs when water, bacteria, or fungi enter the ear canal and cause an infection. Several factors can contribute to the development of this condition, including:
- Excessive moisture: Prolonged exposure to water, such as swimming or excessive sweating, can create a moist environment in the ear canal, facilitating bacterial or fungal growth.
- Trauma or irritation: Scratching the ear canal with sharp objects or improper cleaning techniques can damage the delicate skin lining the ear, making it susceptible to infection.
- Skin conditions: Certain skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis, can disrupt the protective barrier of the ear canal, increasing the risk of infection.
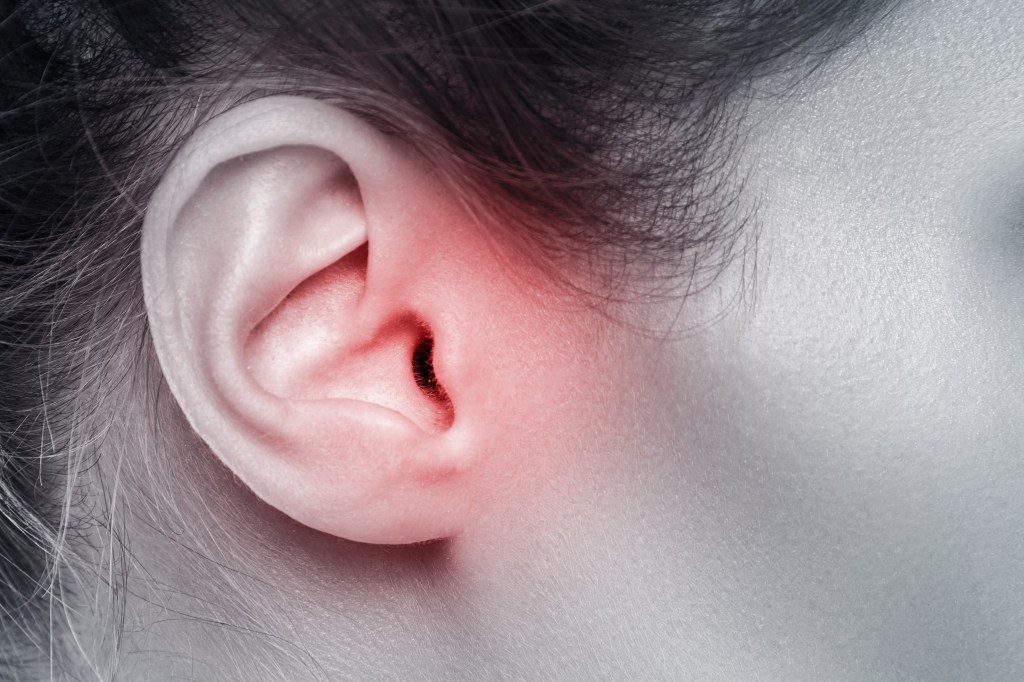
Symptoms of Otitis Externa: The symptoms of otitis externa can vary from mild to severe and typically include:
- Ear pain or discomfort: The infected ear may feel tender, itchy, or painful, especially when touched or when pressure is applied.
- Swelling and redness: The skin in the ear canal may appear red, swollen, and inflamed.
- Drainage: Otitis externa can cause the ear to discharge a yellowish or pus-like fluid.
- Hearing impairment: In some cases, a partial loss of hearing may occur due to the swelling and fluid buildup in the ear canal.
Prevention of Otitis Externa: Preventing otitis externa is essential, especially for individuals prone to frequent ear infections. Here are some preventive measures you can take:
- Keep ears dry: After swimming or bathing, tilt your head to each side to allow water to drain from the ears. Using a towel to gently dry the outer ear can also help prevent excessive moisture.
- Avoid inserting objects: Refrain from inserting cotton swabs, bobby pins, or any other objects into the ear canal, as they can cause irritation or damage.
- Ear protection: If you swim regularly, consider wearing earplugs or a swim cap to prevent water from entering the ear canal.
- Maintain ear hygiene: Clean the outer ear carefully with a soft cloth, but avoid overcleaning or using harsh soaps or chemicals.
Treatment Options for Otitis Externa: If you suspect you have otitis externa, it is crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. The treatment options typically include:
- Medication: Your doctor may prescribe eardrops containing antibiotics or antifungal agents to eliminate the infection. Pain relievers may also be recommended to alleviate discomfort.
- Ear cleaning: In some cases, your doctor may need to clean the ear canal to remove debris, pus, or excessive earwax, allowing the medication to reach the affected area more effectively.
- Self-care measures: Following your doctor’s instructions and practicing good ear hygiene are essential for effective healing. Avoid swimming or getting the ears wet until the infection clears up.
In Conclusion: Otitis externa, or swimmer’s ear, is a common ear infection that can cause pain and discomfort. By understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options, you can take the necessary steps to prevent and manage this condition. Remember, if you suspect you have otitis externa, consult an ENT surgeon for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With proper care, otitis externa can be successfully resolved, allowing you to enjoy a healthy and pain-free ear canal.
4 responses to “A dive into otitis externa: Understanding Swimmer’s ears”
[…] Swimmer’s Ear: Keep ears dry after swimming by gently tilting your head and shaking out water. Avoid trying to clean ears with ear buds or Q tips. […]
LikeLike
[…] Swimmer’s ear (otitis externa): An infection of the outer ear canal, commonly caused by excess moisture and bacteria. […]
LikeLike
[…] of the most common water-related ENT issues is swimmer’s ear, also known as otitis externa. This is an infection of the outer ear canal, often caused by […]
LikeLike
[…] in the ear canal, which can encourage the growth of bacteria and fungi, leading to ear infections (otitis externa or “swimmer’s ear“). Sharing earphones further increases this […]
LikeLike